
The intersection of Minimalism and Sustainability
In an era characterized by environmental concerns and the desire for simplicity, the principles of minimalism and sustainability in architecture have become increasingly important. This article explores the intersection of these two concepts and highlights how architects embrace minimalist design principles to create a sustainable built environment where efficiency, functionality, and environmental protection are paramount.
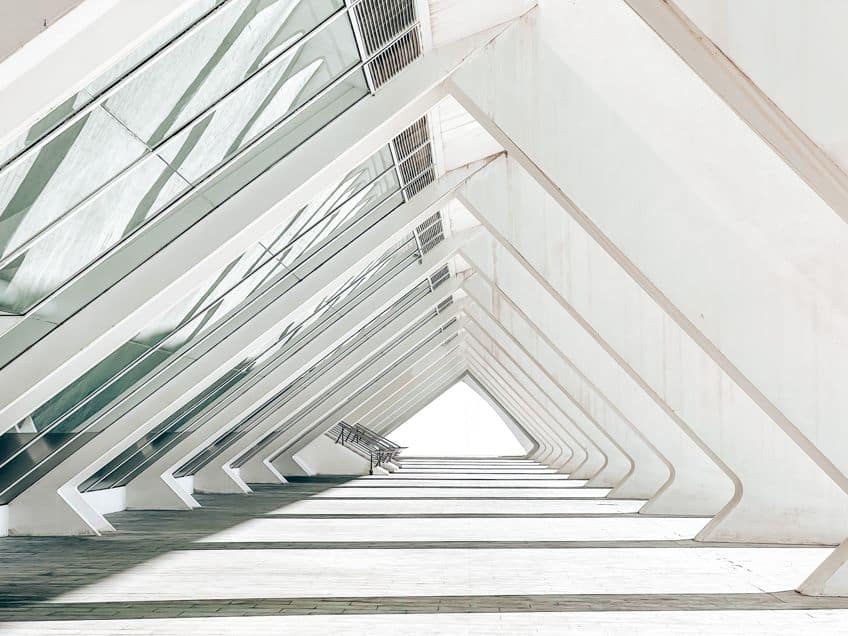
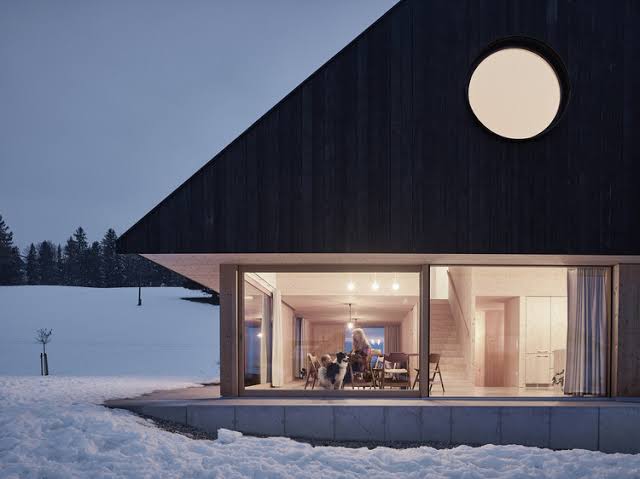
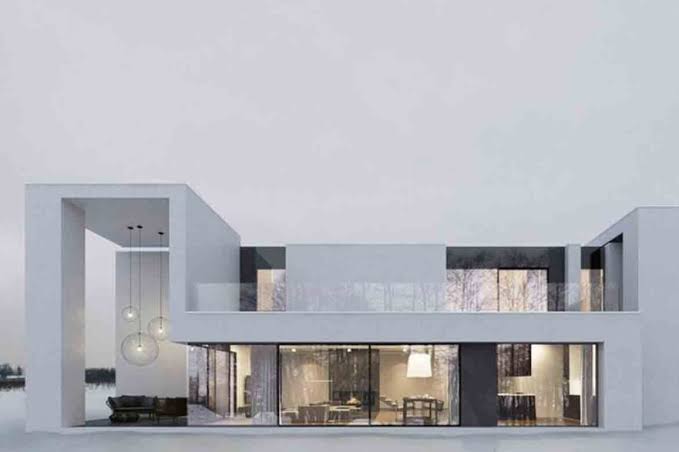
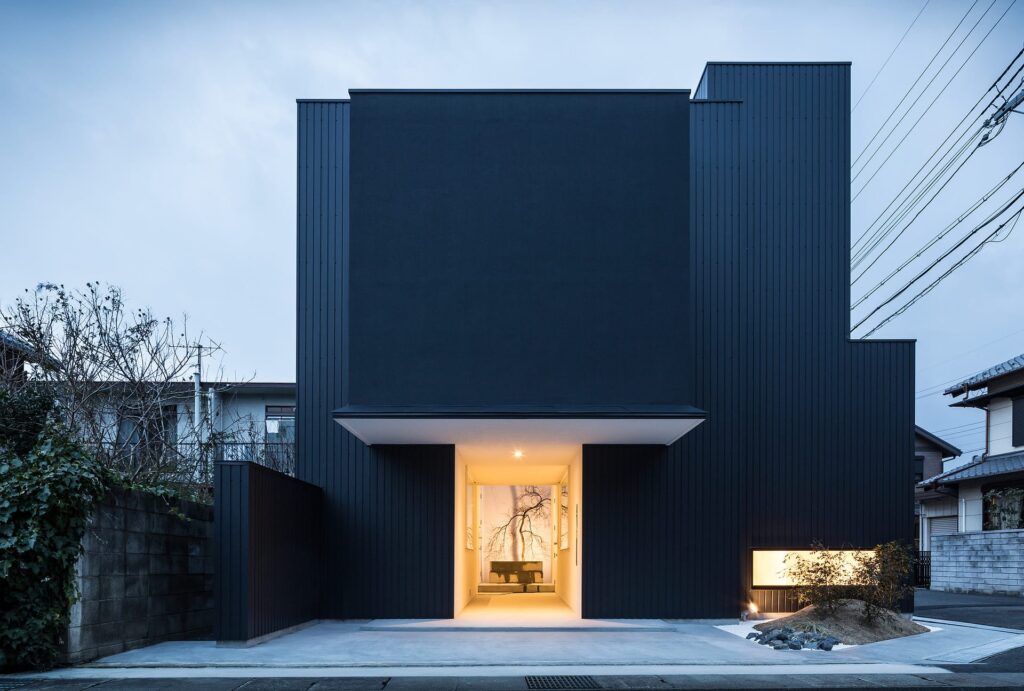
Architectural minimalism is characterized by simplicity, clean lines, and a focus on the essential elements. Architects try to create clean and practical spaces, using as few decorations and materials as possible. Minimalist architecture combines with its basic design elements a sense of peace, clarity, and harmony in built environments. This approach not only increases the aesthetic appeal of buildings but also promotes efficient use of resources and space.
Material selection plays a critical role in both. minimalism and patience. Minimalist architecture often favors natural materials such as wood, stone, and glass for their timeless appeal and natural beauty. Sustainable architecture takes this a step further, prioritizing renewable, recyclable, and locally sourced materials. From reclaimed wood and recycled metal to impact-resistant concrete and eco-friendly insulation, architects use a wide range of sustainable materials to create buildings that are both aesthetically pleasing and environmentally friendly.
Sustainability is a key aspect of today’s architectural practice as climate change and depletion of natural resources urgently need to be addressed. Sustainable architecture aims to minimize environmental impact throughout the life cycle of a building, from design to construction to use and demolition. The main principles are energy efficiency, use of renewable materials, waste reduction, and consideration of the local climate and context. By integrating sustainability strategies into the design, architects can create buildings that are environmentally friendly, sustainable, and cost-effective.
Minimal architecture and sustainable development go hand-in-hand to promote efficiency in building design. Minimalist principles such as simplicity and space optimization are naturally compatible with sustainable practices such as passive solar design, natural ventilation, and daylighting. By maximizing natural light, minimizing energy consumption optimizing building orientation, architects can reduce reliance on artificial lighting and HVAC systems, resulting in lower operating costs and carbon emissions.
The guiding principle: Minimalism is an idea of “less is more” that emphasizes quality over quantity and sustainability over single use. Sustainable architecture follows this philosophy by designing buildings that are built to last and adapt to changing needs over time. By prioritizing sustainability, flexibility, and longevity, architects can reduce the environmental impact of construction and minimize the need for future repairs or demolitions, thereby conserving resources and reducing waste.
Minimalism and sustainability are not just design trends, but important principles that will guide the future of architecture. Embracing simplicity, efficiency, and environmental responsibility, architects have the power to create buildings that improve the quality of life for residents and contribute to a greener, more sustainable planet. By combining minimalist design principles with sustainable strategies, architects can pave the way for a more sustainable, just, and harmonious built environment for future generations.






One Comment
Abhinav Solanki
Courtly written